
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags or transponders are small devices that utilize low-power radio waves to receive, store, and transmit data to nearby readers. RFID tags are comprised of the following main components: a microchip or integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate or protective material layer that holds all the components together.
There are three basic types of RFID tags: passive, active, and semi-passive or battery-assisted passive (BAP). Passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source, rather, they are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader. Active RFID tags have their own transmitter and power source on-board the tag. Semi-passive or battery-assisted passive (BAP) tags are comprised of a power source incorporated into a passive tag configuration. Additionally, RFID tags operate in three frequency ranges: Ultra-High Frequency (UHF), High Frequency (HF), and Low Frequency (LF).
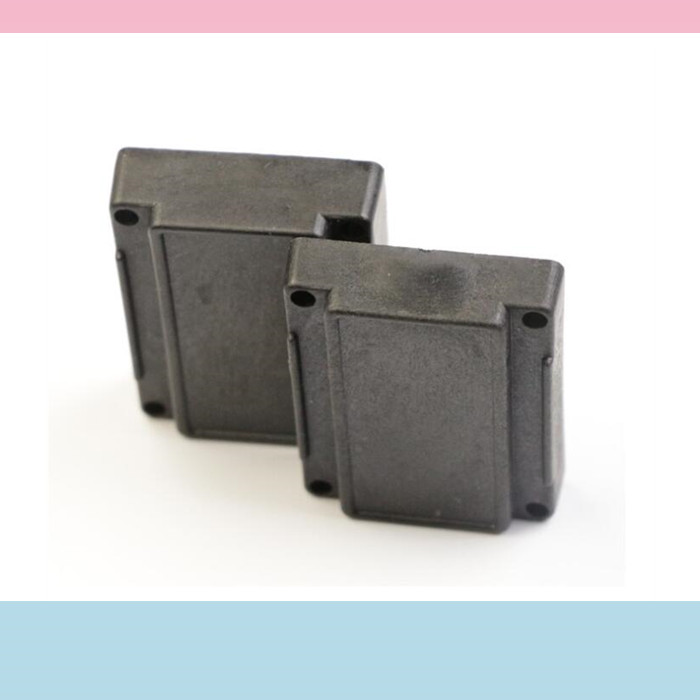
RFID tags can be affixed to a variety of surfaces and are widely available in various sizes and designs. RFID tags also come in a wide array of form factors including but not limited to wet inlays, dry inlays, labels, wristbands, hard tags, cards, stickers, and fobs. atlasRFIDstore offers brand name RFID tags suitable for many different environments and applications such as logistics, supply chain, race timing, access control, laundry management, tool tracking, and IT asset tracking.
Whether the industry is manufacturing & logistics, construction, oil & gas, utilities, IT & office management, or government & defense, there’s a passive, active, custom, embedded or sensor tag that’s fit for purpose — and DO RFID TAG manufacturer can supply it.
Different types of RFID tags
There are many different ISO standards, protocols, and physical differences between various RFID tag types. Choosing compatible readers and tags can be tricky, especially for an RFID novice. For the purposes of this explanation, we’ll only focus on passive RFID, specifically, Low-Frequency (LF), High-Frequency (HF), Near Field Communication (NFC), and NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF). For a little bit of background, here are some examples of how each type of RFID tag is used.
Passive RFID examples:
♦ Employee and/or Student Access control cards (LF or HF)
♦ Nametags / Badges / Wristbands / Tickets for conferences or events (NFC)
♦ Animal tagging (LF)
♦ Marketing posters that pull up a specific website when the tag is scanned (NDEF)
RFID Tag Technology
Within passive RFID technology, there are three main RFID tag, RFID tag reader technologies on the market today, named after their respective frequency bands: low-frequency (LF, 125 kHz or 134 kHz), high-frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz), and ultra-high-frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz). In most instances, each type of passive RFID tag (LF, HF, or UHF) can only be read by the type of passive RFID reader. For instance, usually, an LF reader will only be able to read an LF RFID tag; it will not able to read an HF or a UHF tag.
Further, within each passive RFID frequency band, there are a handful of ISO standards that need to be followed in order to facilitate reader-to-tag communication. Here are the major standards for each passive RFID frequency band:
Low Frequency:
♦ ISO 14223
♦ ISO/IEC 18000-2
High Frequency:
♦ ISO 15693
♦ ISO/IEC 14443 A
♦ ISO/IEC 14443 B
♦ ISO/IEC 18092
Ultrail High Frequency:
♦ ISO18000-2




If you want to ask anything just fill in the form below and send us. We will contact you within 12 hours.

DO RFID TAG manufacturer able custom RFID tags for inventory and asset tracking, such as file servers or rental equipment, allow for a quick inventory and knowledge of where assets are located.
More >>
Do you know the rfid 125khz sticker ? TK4100,EM4100O sticker
More >>